Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) technologies, alongside rapid and deep emissions reductions, are critical to prevent dangerous climate change. However, as the CDR market scales, the safety, integrity and efficacy of these interventions are paramount. A fundamental challenge lies in establishing robust and credible monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) frameworks that inspire widespread trust among all stakeholders, from policymakers and investors to the public and scientific community. This is especially true for enhanced rock weathering (ERW), a complex open-system pathway with many remaining open research questions. This necessitates a radical shift towards comprehensive data transparency and shared learnings to advance the field as a whole.
Building trust in nascent CDR technologies, particularly for pathways like ERW, hinges on verifiable data and transparent methodologies. The voluntary carbon market has historically faced criticism regarding credit quality and additionality, underscoring the urgent need for heightened integrity. Transparency is not merely good practice; it is a prerequisite for a credible and accountable carbon market. Data transparency facilitates shared learnings, supporting the widespread scale-up of high-quality CDR.
InPlanet has consistently been at the forefront of ERW innovation, pioneering operations in Brazil under tropical and subtropical conditions and issuing the world’s first carbon credits with ERW. Today, InPlanet announced another significant milestone: it has become the first company to share its commercial CDR data through the Cascade Climate ERW Data Quarry. This comprehensive dataset originates from InPlanet’s Project Serra da Mantiqueira in Brazil, the same project for which the company issued ERW carbon credits with Isometric earlier this year. Crucially, the underlying data for this credit issuance is also publicly available on the Isometric registry.
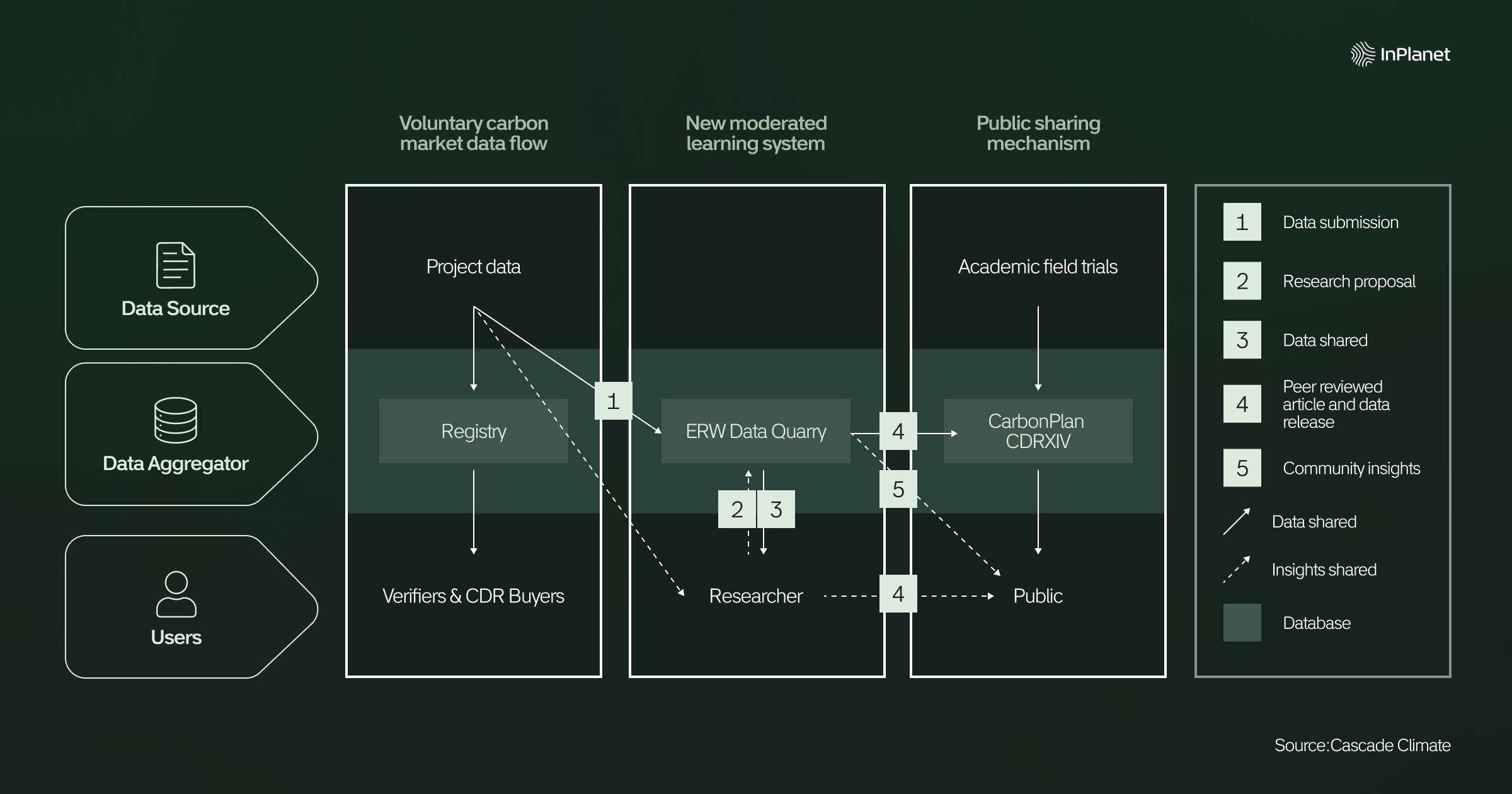
This unprecedented move by InPlanet, making commercial CDR data available to academics via the ERW Data Quarry, represents a step towards fostering the radical transparency required for the responsible growth of the CDR industry. Academics can now apply to access the dataset, allowing for further research while supporting learning. The schematic below depicts how this process works. This initiative directly addresses the call for more empirical data from commercial deployments to inform scientific research and enhance confidence in CDR technologies.
We would encourage other CDR project developers, particularly those operating in nascent pathways to follow in InPlanet’s footsteps. Access to commercial deployment data will undoubtedly accelerate research and development, facilitate the creation of more accurate and robust MRV protocols, and ultimately provide the crucial learnings needed to reduce existing uncertainty and close fundamental research gaps. This collective effort is indispensable for rapidly advancing the entire field of ERW and ensuring its credible contribution to global climate change mitigation.
Authored by:
Dr. Junyao Kang
Data Analysis & Modeling Lead
Dr. Christina Larkin
Head of Science & Research